Precision casting, also known as investment casting or lost-wax casting, is a versatile manufacturing process used to create intricate and high-quality metal components. From aerospace to jewelry, Precision casting finds applications in various industries due to its ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances. Mastering this technique requires attention to detail and a systematic approach. In this guide, we'll walk you through the Precision casting process step by step.
Step 1: Design and Pattern Creation The process begins with the creation of a pattern, typically made from wax or another easily meltable material. The pattern is an exact replica of the final part, including all its intricate details. CAD software or traditional sculpting techniques can be used to design the pattern. Once the pattern is ready, it is attached to a gating system, which facilitates the flow of molten metal during casting.
Step 2: Assembly and Investment The pattern, along with the gating system, is then attached to a central wax rod to form a tree-like structure called a sprue. This assembly is dipped repeatedly into a ceramic slurry, allowing a ceramic shell to build up around the wax pattern. After each dip, the shell is coated with a fine sand or stucco to create a strong and heat-resistant mold. This process is repeated several times until the desired shell thickness is achieved.
Step 3: Dewaxing and Preheating Once the ceramic shell is dry and hardened, the entire assembly is placed in an autoclave or furnace to melt out the wax, leaving behind a cavity in the shape of the original pattern. The ceramic shell is then preheated to a specific temperature to prepare it for the pouring of molten metal.
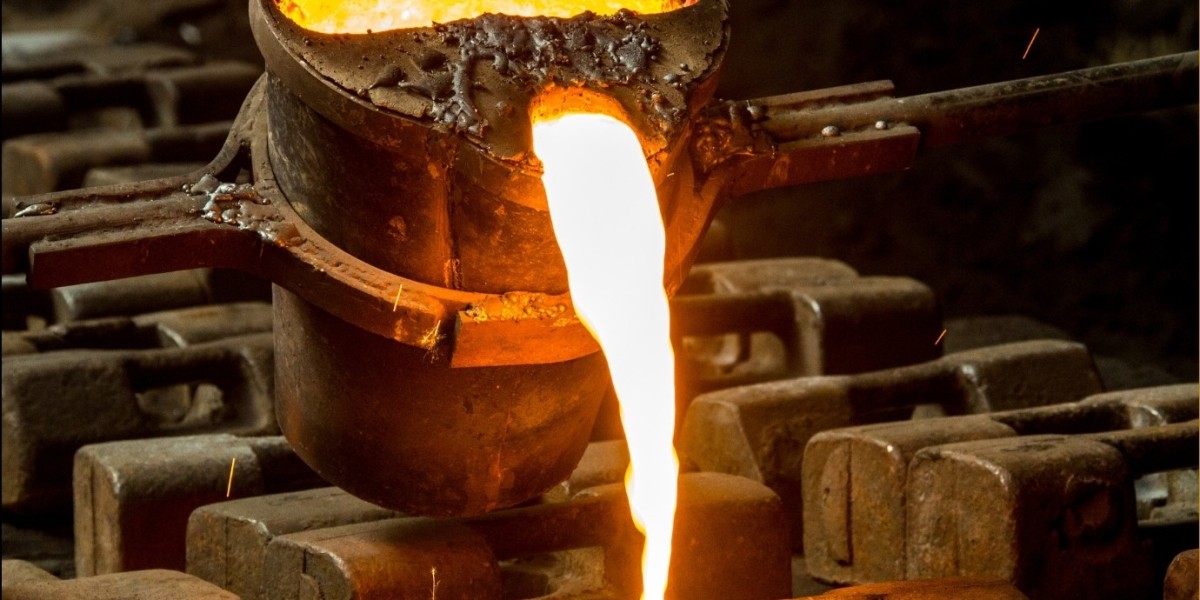
Step 4: Casting With the ceramic shell preheated, it is ready for casting. Molten metal, typically aluminum, bronze, or stainless steel, is poured into the cavity using gravity or vacuum-assisted methods. The metal fills the cavity and takes on the shape of the pattern.
Step 5: Cooling and Finishing After the metal has solidified, the ceramic shell is broken away, revealing the cast metal component. Any excess material or imperfections are removed through machining, grinding, or sandblasting. Finally, the part is inspected for quality and accuracy.
Step 6: Post-Processing Depending on the application, the cast part may undergo additional treatments such as heat treatment, surface finishing, or assembly with other components before it is ready for use.
Precision casting offers unmatched flexibility and precision in producing complex metal components. By following these steps and paying attention to detail, you can master the Precision casting process and unlock its full potential in your manufacturing endeavors.