Title: Understanding Osteoarthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
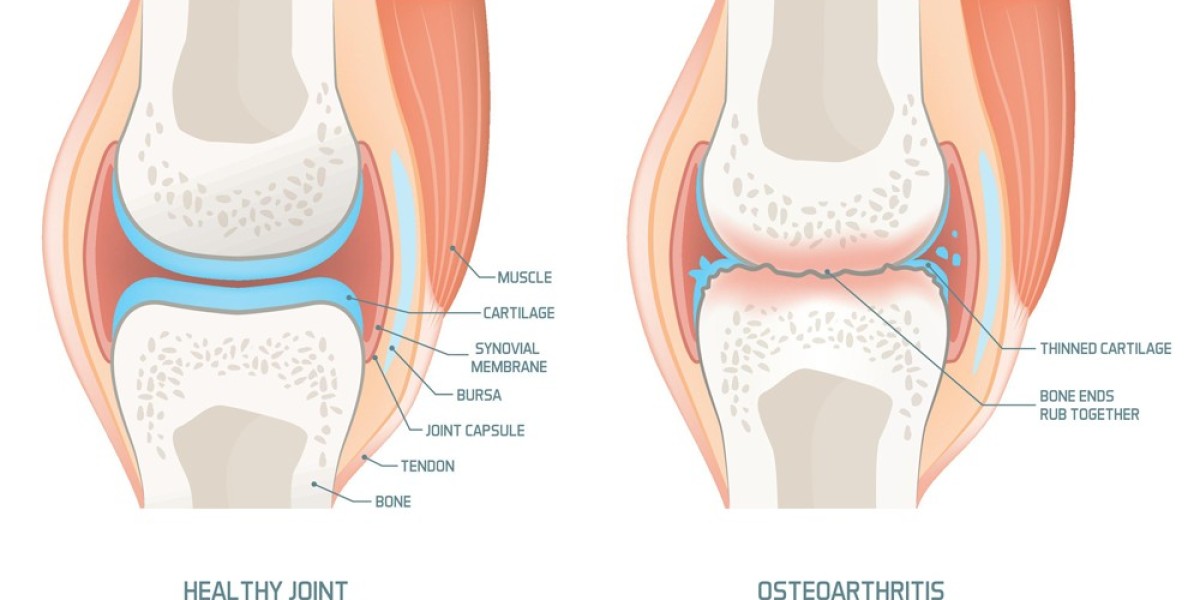
Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent joint disorder affecting millions worldwide, characterized by the degeneration of cartilage in joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While often associated with aging, OA can also develop due to various factors, including genetics, joint injury, and obesity. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for osteoarthritis is crucial for managing this condition effectively and improving quality of life.
Causes of Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis develops when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones in the joints gradually breaks down over time. Several factors contribute to this degeneration, including:
- Age: As people age, the risk of developing osteoarthritis increases. Wear and tear on the joints over the years can lead to cartilage damage and eventual OA.
- Joint Injury: Previous joint injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the affected joint later in life.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips, increasing the risk of developing OA.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can predispose individuals to osteoarthritis. Certain genetic variations may affect the strength and integrity of cartilage, contributing to its breakdown.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis: The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary in severity and typically develop gradually over time. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Joint Pain: Pain in the affected joint, which may worsen with movement and improve with rest.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the joint, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking in the morning.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the affected joint fully, leading to a reduced range of motion.
- Joint Swelling: Swelling and tenderness around the affected joint may occur, particularly during flare-ups.
- Grating Sensation: A grating sensation or the sound of bone rubbing against bone may be felt during joint movement.
Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis: While there is currently no cure for osteoarthritis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve joint function. These include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide temporary relief.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce stress on weight-bearing joints. Low-impact activities, such as swimming and cycling, are often recommended for individuals with osteoarthritis.
- Assistive Devices: Using assistive devices, such as braces, can help support the affected joint and reduce strain during daily activities.
- Surgery: In severe cases of osteoarthritis where conservative treatments have failed, surgical options such as joint replacement surgery may be considered to replace the damaged joint with a prosthetic implant.
Conclusion: Osteoarthritis is a common joint disorder that can significantly impact quality of life, but with proper management, its symptoms can be effectively controlled. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for osteoarthritis, individuals can work with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to their needs, allowing them to stay active and maintain mobility for years to come.