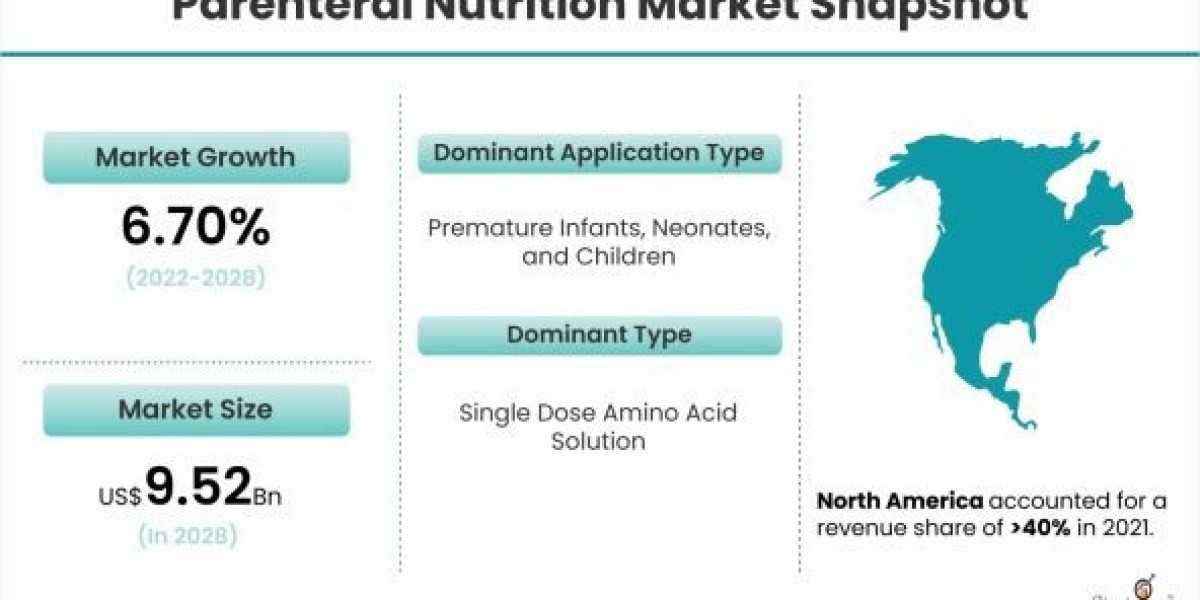
The Parenteral Nutrition Market is segmented by Product Type (Carbohydrates, Parenteral Lipid Emulsion, Single Dose Amino Acid Solution, Trace Elements, Vitamins, and Minerals), Application (Premature Infants, Neonates and Children, Geriatrics, Chronic Disease Patients), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World).
The Parenteral Nutrition Market represents a crucial frontier in healthcare, offering vital insights into sustaining patients unable to receive adequate nourishment orally. This market's evolution is driven by a fundamental understanding: for some individuals, intravenous feeding becomes a lifeline, providing essential nutrients when oral intake is insufficient or impossible.
Insights into this market reveal a multifaceted approach to patient care. Parenteral nutrition isn't merely a substitute; it's a tailored solution. It caters to diverse patient needs, from those undergoing extensive surgeries unable to eat, to individuals with severe malabsorption or digestive disorders hindering nutrient absorption.
The market's insights emphasize the critical role of customization. Healthcare providers analyze patient profiles meticulously, crafting personalized nutrition solutions. From macronutrient composition adjustments to specialized formulations, precision is paramount to meet individual metabolic demands and promote healing.
Furthermore, the market's advancements underscore continuous innovation. Ongoing research explores new formulations, delivery methods, and technology integration to enhance safety, efficacy, and patient comfort.
Beyond being an alternative to oral intake, insights into the Parenteral Nutrition Market highlight its indispensable role in critical care, rehabilitation, and chronic conditions. It represents a lifeline for patients, ensuring they receive vital nutrition, fostering recovery, and improving overall health outcomes where traditional feeding methods fall short.