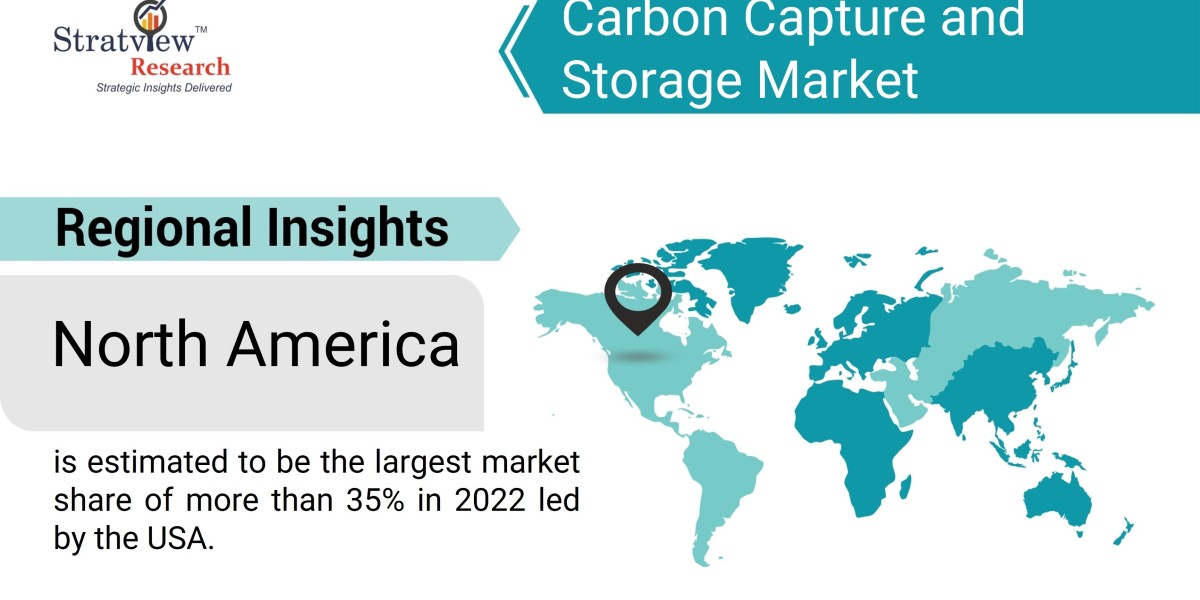
According to Stratview Research, the carbon capture and storage market was estimated at USD 3.57 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 5.92% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 5.04 billion in 2028.
As the world grapples with the urgency of mitigating climate change, the Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) market has emerged as a critical player in the quest for sustainable solutions. This article delves into the dynamic landscape of the CCS market, exploring innovative technologies and strategies that hold the potential to reshape the future of carbon capture, storage, and the fight against global warming.
The Imperative of Carbon Capture and Storage:
Carbon Capture and Storage is a vital technology in the arsenal of climate change mitigation strategies. It involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes and power generation, transporting it, and securely storing it underground to prevent its release into the atmosphere.
Innovations in Capture Technologies:
Capturing tomorrow begins with innovations in carbon capture technologies. Novel approaches such as post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion are continuously evolving to enhance efficiency and reduce the costs associated with capturing CO2 emissions from diverse sources.
Direct Air Capture (DAC) Technologies:
The exploration of tomorrow's carbon capture landscape includes Direct Air Capture (DAC) technologies. These innovations aim to capture CO2 directly from the ambient air, offering a versatile solution for addressing emissions from dispersed sources and industries that are challenging to decarbonize.
Advancements in Storage Techniques:
Efficient storage is a cornerstone of CCS success. Innovations in storage techniques, including geological storage in depleted oil and gas reservoirs or deep saline formations, are being refined for optimal security and permanence. These advancements ensure that captured carbon remains sequestered underground for the long term.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Synergies:
Innovative strategies in the CCS market include synergies with Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR). By utilizing captured CO2 to enhance oil extraction from depleted fields, this approach not only sequesters carbon but also extends the productive life of oil reservoirs, creating a dual-purpose and economically viable solution.
Utilizing Biomass for Negative Emissions:
Exploring tomorrow's possibilities involves integrating CCS with biomass energy generation. Biomass can be used as a renewable energy source, and when combined with CCS, it achieves negative emissions by removing more CO2 from the atmosphere than it generates during combustion.
Floating Carbon Capture Technologies:
The future of carbon capture ventures into the seas with floating carbon capture technologies. These innovative solutions involve deploying floating platforms equipped with carbon capture facilities in strategic locations, capturing CO2 directly from the ocean or adjacent industrial facilities.
Decentralized Carbon Capture Networks:
Tomorrow's CCS landscape envisions decentralized carbon capture networks. Instead of relying on large centralized facilities, smaller-scale capture units strategically positioned near emission sources can offer more flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility for diverse industries.
Carbon Capture as a Service (CCaaS):
Innovative business models are emerging with the concept of Carbon Capture as a Service (CCaaS). Companies are exploring ways to provide carbon capture solutions as a service, allowing businesses to outsource their carbon reduction efforts and focus on core operations.
Blockchain for Transparent Carbon Accounting:
The innovations in the CCS market extend to transparent carbon accounting through blockchain technology. Blockchain ensures traceability and accountability in carbon capture and storage projects, providing a trustworthy framework for monitoring and verifying carbon reduction efforts.
Government Incentives and Policies:
Capturing tomorrow also involves innovative government incentives and policies that encourage the widespread adoption of CCS technologies. Financial support, tax credits, and regulatory frameworks are crucial elements in fostering an environment conducive to the growth of the CCS market.
Public-Private Collaborations:
The dynamic landscape of CCS is shaped by collaborative efforts between the public and private sectors. Innovations often arise from partnerships that leverage the expertise, resources, and funding from both governmental bodies and private enterprises to accelerate the development and deployment of CCS technologies.
Conclusion:
Capturing tomorrow in the realm of carbon capture and storage requires a commitment to continuous innovation, collaboration, and the pursuit of diverse solutions. The dynamic landscape of the CCS market holds the promise of transforming how we approach carbon reduction, paving the way for a sustainable and resilient future. As technological advancements and strategic initiatives unfold, the vision of a low-carbon world becomes increasingly attainable, and the journey towards a more sustainable tomorrow gains momentum.