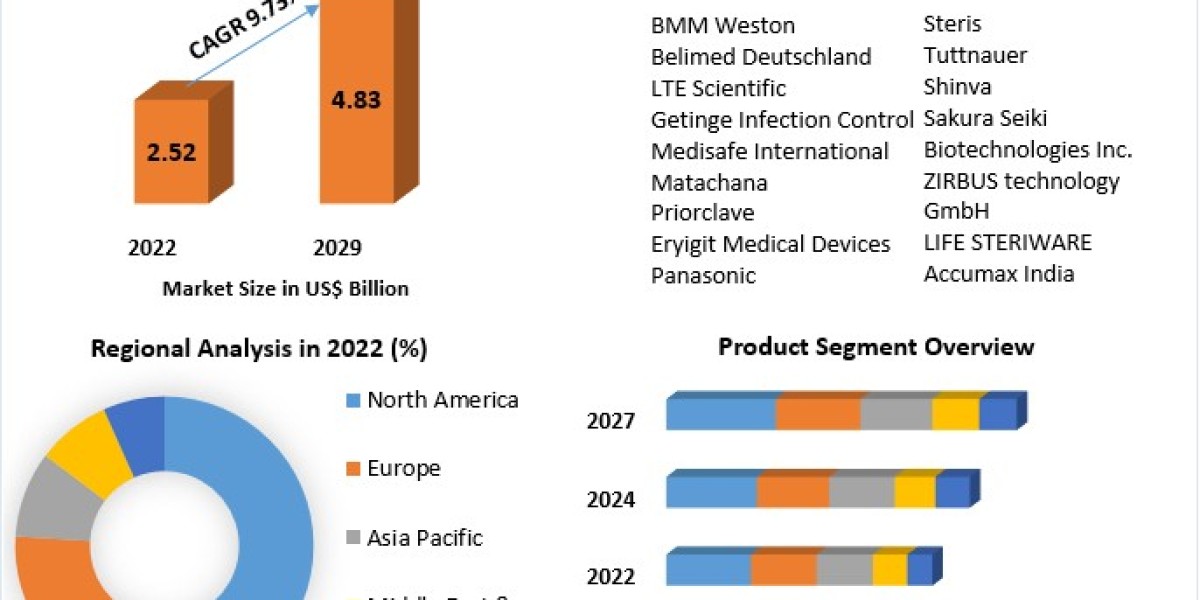
Sample pretreatment kits play a crucial role in various analytical and scientific processes by ensuring the effective preparation of samples for analysis. Whether it's in molecular biology, environmental science, or analytical chemistry, proper sample pretreatment can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of results. This guide aims to provide a detailed overview of Sample Pretreatment Kits, their importance, and how to effectively utilize them for optimal sample preparation.
Understanding Sample Pretreatment Kits: Sample Pretreatment Kits typically include a range of reagents, buffers, columns, and other materials designed to facilitate the purification, concentration, and modification of samples before analysis. These kits are tailored to specific sample types and analysis techniques, ensuring consistency and reproducibility in results.
Importance of Sample Pretreatment: Proper sample pretreatment is essential for removing impurities, reducing matrix effects, and enhancing analyte detection sensitivity. It helps to improve the signal-to-noise ratio, minimize interference, and ensure accurate quantification of target analytes. Sample pretreatment also enables the selective extraction of compounds of interest from complex matrices, thereby streamlining the analytical process.
Choosing the Right Kit: When selecting a sample pretreatment kit, consider the nature of your sample, the analytes of interest, and the desired analysis technique. Look for kits that are compatible with your sample type (e.g., biological fluids, environmental samples, food matrices) and offer the required selectivity and sensitivity for your application.
Key Components of Sample Pretreatment Kits: Sample Pretreatment Kits typically include:
- Extraction buffers or solvents for sample preparation.
- Solid-phase extraction (SPE) or liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) columns for purification and concentration.
- Binding materials (e.g., silica, resins) for selective analyte capture.
- Wash solutions to remove unwanted contaminants.
- Elution buffers for the recovery of purified analytes.
- Quality control standards and protocols for validation.
Best Practices for Sample Pretreatment:
- Follow the kit instructions carefully to ensure reproducible results.
- Optimize conditions such as pH, temperature, and incubation time for maximum efficiency.
- Use appropriate controls to monitor the efficiency of the pretreatment process.
- Maintain cleanliness and sterility to prevent contamination.
- Validate the pretreatment method to ensure accuracy and precision.
- Store reagents and samples according to manufacturer recommendations to maintain stability.
Conclusion: Sample Pretreatment Kits are indispensable tools for enhancing the quality and reliability of analytical data. By understanding their importance, selecting the right kit, and following best practices, researchers can achieve optimal sample preparation and obtain accurate and reproducible results in their analyses.