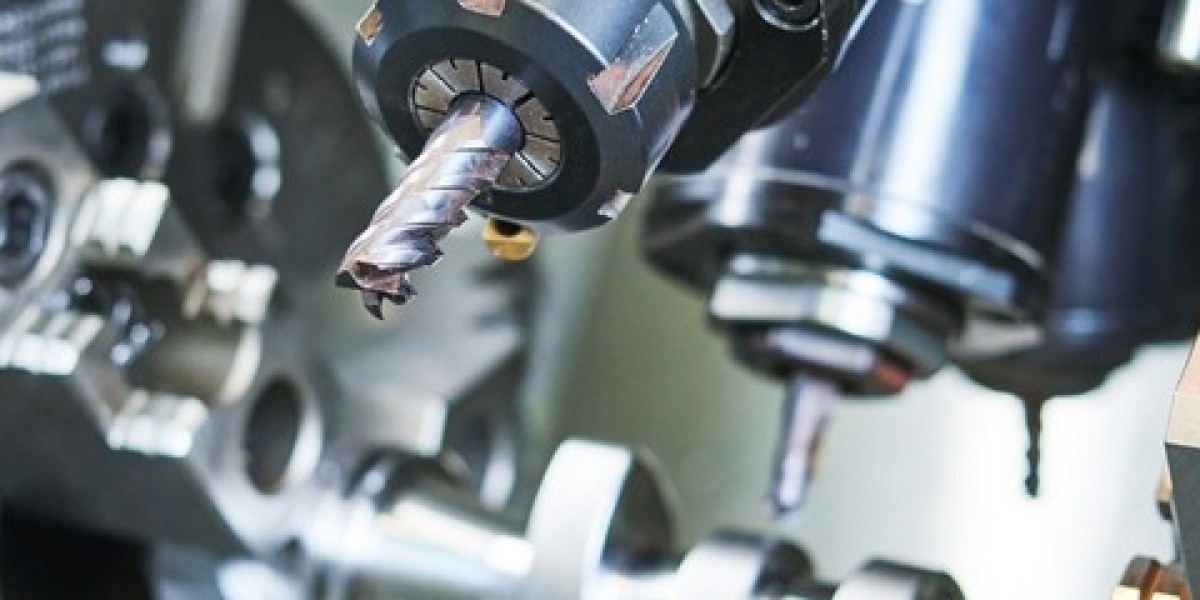
Steel machining is a critical process in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Achieving precision and efficiency in steel machining requires a combination of expertise, proper equipment, and meticulous planning. This guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into steel machining, covering techniques, tools, and best practices to enhance productivity and quality.
Understanding Steel Properties: Before diving into machining, it's crucial to understand the properties of steel being worked with. Factors such as hardness, composition, and grain structure significantly influence machining processes. Different steel alloys may require specific cutting speeds, feeds, and tool materials for optimal results.
Selecting the Right Tools: Choosing the appropriate cutting tools is paramount for successful steel machining. High-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and ceramic tools are common choices, each offering unique advantages based on the application. Considerations such as tool geometry, coating, and wear resistance play vital roles in tool selection.
Machining Techniques: a. Turning: Turning is a fundamental machining operation for creating cylindrical components. Employ techniques like roughing, finishing, and profiling to achieve desired dimensions and surface finish. b. Milling: Milling operations involve removing material using rotary cutters. Utilize strategies such as face milling, end milling, and slotting to produce complex shapes with precision. c. Drilling: Drilling is essential for creating holes in steel components. Optimize drilling parameters such as speed, feed, and coolant usage to prevent tool wear and maintain accuracy. d. Grinding: Grinding is ideal for achieving tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes. Utilize grinding wheels with appropriate abrasives and grit sizes for efficient material removal.
Tooling Maintenance: Regular maintenance of cutting tools is crucial for prolonging tool life and maintaining machining accuracy. Implement proper lubrication, cooling, and tool inspection routines to detect wear and prevent premature tool failure.
Safety Considerations: Safety should always be a top priority in steel machining operations. Ensure operators are trained in proper machine operation, use personal protective equipment (PPE), and adhere to safety protocols to minimize risks of injury.
Conclusion: Mastering steel machining requires a blend of knowledge, skill, and attention to detail. By understanding steel properties, selecting the right tools, employing appropriate techniques, and prioritizing safety, machinists can achieve optimal results in terms of precision, efficiency, and quality. Continual learning and adaptation to advancements in machining technology will further enhance productivity and competitiveness in steel machining processes.