Introduction
In today's dynamic work environment, lone workers are increasingly common across various sectors such as delivery, healthcare, maintenance, and public service. While these workers often operate independently, they face unique risks, one of the most prevalent being dog bites. Ensuring the safety of lone workers from dog attacks is not only a moral obligation but also a legal one. This comprehensive guide aims to provide detailed strategies for preventing dog bites for lone workers, emphasizing practical measures, training, and policies.
Understanding the Risks
Who Are Lone Workers?
Lone workers dog bite prevention are individuals who perform their job duties in isolation from other workers, without direct supervision or company support. This includes delivery drivers, postal workers, healthcare providers making home visits, utility workers, and more. The isolated nature of their work makes them vulnerable to various hazards, including dog bites.
The Prevalence of Dog Bites
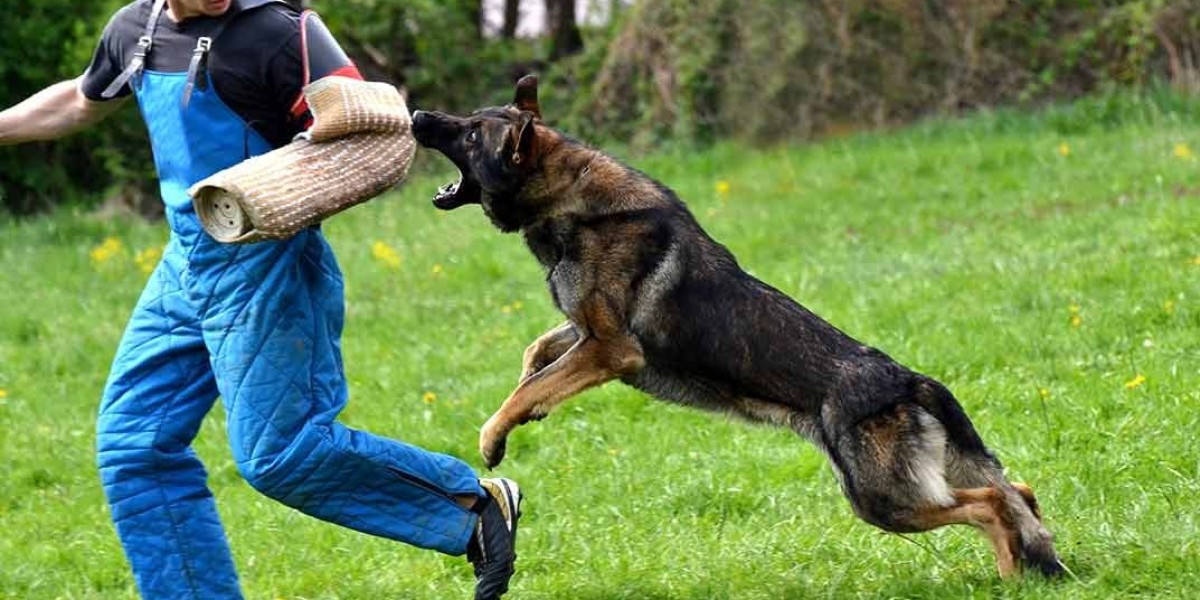
Statistics reveal that dog bites are a significant concern for lone workers. For example, postal workers in the United States reported over 5,800 dog bites in 2020 alone. The consequences of dog bites can range from minor injuries to severe trauma, leading to lost workdays, medical expenses, and emotional distress.
Preventative Measures
Training and Education
Proper training is crucial for preventing dog bites. Employers should ensure that all lone workers receive comprehensive training on how to handle encounters with dogs. This training should include:
Recognizing Dog Behavior: Understanding signs of aggression or anxiety in dogs, such as growling, barking, or body posture.
Safe Approaches: Techniques for safely approaching properties where dogs may be present.
Avoidance Strategies: Methods for avoiding direct interaction with dogs, such as staying outside gates or fences.
Use of Protective Equipment
Employers should provide protective equipment to lone workers, which may include:
Dog Repellents: Non-harmful sprays or devices that can deter dogs from approaching.
Protective Clothing: Long sleeves, gloves, and sturdy boots can minimize injury if a dog bite occurs.
Communication Devices: Portable alarms or whistles can alert others in case of an emergency.
Establishing Safety Protocols
Developing and implementing clear safety protocols is essential. These should cover:
Risk Assessment: Regular assessment of areas where lone workers operate to identify potential dog hazards.
Reporting Procedures: Clear guidelines on how to report dog encounters or bites, ensuring prompt action and support.
Emergency Response Plans: Defined steps for lone workers to follow if they are bitten or threatened by a dog, including seeking medical attention and notifying supervisors.
Technological Solutions
GPS Tracking and Monitoring
Modern technology can significantly enhance the safety of lone workers. GPS tracking devices allow real-time monitoring of worker locations, enabling quick response in case of an incident. These devices can also have built-in alert systems to notify supervisors if a worker is in distress.
Mobile Safety Apps
Safety apps designed for lone workers can offer features such as:
Check-In Systems: Regular check-ins to confirm the worker's safety.
Panic Buttons: Immediate alerts to supervisors or emergency services in case of danger.
Incident Reporting: Easy reporting of dog sightings or attacks, streamlining the response process.
Behavioral Strategies
Understanding Dog Behavior
Educating lone workers on dog behavior is critical. Dogs typically show signs before biting, and understanding these signs can prevent an attack. Common behaviors to watch for include:
Aggressive Posture: Raised hackles, direct staring, and stiff body language.
Fearful Behavior: Cowering, tail tucking, and avoiding eye contact.
Territorial Aggression: Barking, growling, and lunging at perceived intruders.
Approaching Homes and Properties
When approaching homes or properties where dogs might be present, lone workers should:
Make Noise: Announce their presence by knocking or ringing the bell before entering a yard.
Avoid Sudden Movements: Move slowly and avoid startling dogs.
Keep a Barrier: Use items such as bags or equipment to create a barrier between themselves and the dog.
Responding to Dog Encounters
If a dog approaches, workers should:
Stay Calm: Avoid yelling or running, as this can trigger a dog's chase instinct.
Use Commands: Firmly say "No" or "Go home" to assert dominance without escalating aggression.
Back Away Slowly: If the dog does not retreat, slowly back away while maintaining eye contact.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Employer Responsibilities
Employers have a legal obligation to protect their lone workers. This includes:
Risk Management: Conducting thorough risk assessments and implementing appropriate safety measures.
Training Programs: Providing regular training sessions and updates on dog bite prevention.
Support Systems: Offering medical, psychological, and legal support to workers who suffer dog bites.
Worker Rights
Lone workers have the right to a safe working environment. They should:
Receive Training: Be adequately trained on how to handle dog encounters.
Report Incidents: Feel empowered to report any dog-related incidents without fear of retribution.
Access Resources: Have access to necessary resources and support following a dog bite.
Conclusion
Preventing dog bites for lone workers is a multifaceted challenge that requires a combination of training, protective measures, behavioral strategies, and technological solutions. By understanding the risks and implementing comprehensive safety protocols, employers can create a safer working environment for their lone workers. Proactive measures not only protect employees but also enhance overall operational efficiency and legal compliance.