Breast augmentation, commonly known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at enhancing the size and shape of the breasts. This treatment is one of the most popular cosmetic surgeries worldwide, chosen by women for various reasons ranging from aesthetic desires to reconstructive needs following medical conditions.
Why Consider Breast Augmentation?
Women opt for breast augmentation for numerous reasons, including:
- Enhancement of Breast Size and Shape: Many women seek augmentation to achieve fuller breasts or to correct asymmetry.
- Post-Pregnancy Restoration: After childbirth and breastfeeding, breasts can lose volume and shape. Augmentation can restore their pre-pregnancy appearance.
- Reconstruction Post-Mastectomy: For breast cancer survivors, reconstruction can be a critical part of the healing process, helping them regain a sense of normalcy and confidence.
- Self-Confidence Boost: Enhancing physical appearance often translates to improved self-esteem and body image.
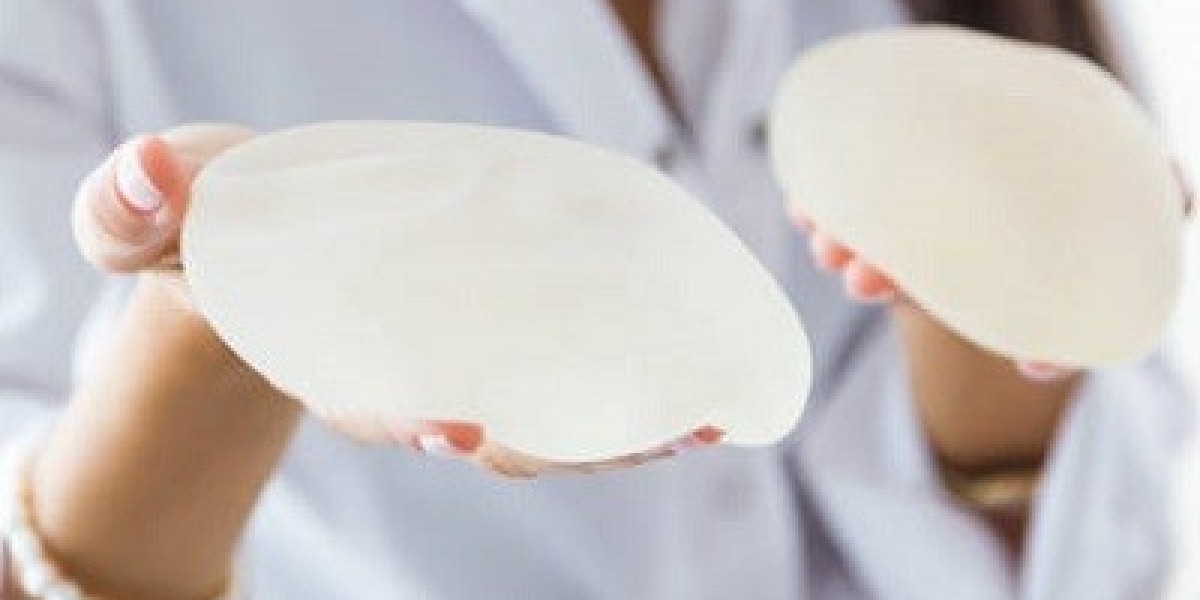
Types of Breast Implants:
There are two primary types of breast implants:
Saline Implants: These are filled with sterile salt water. They are inserted empty and then filled once in place. Saline implants offer a uniform shape, firmness, and feel. Should the implant shell leak, a saline implant will collapse, and the saline will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body.
Silicone Implants: These are pre-filled with silicone gel, which feels more like natural breast tissue. If a silicone implant leaks, the gel may remain within the implant shell or escape into the breast implant pocket. Leaking silicone implants might not collapse, hence a regular check-up is recommended to ensure proper function.
The Procedure:
The breast augmentation procedure typically involves the following steps:
Consultation: Discussing goals, expectations, and medical history with a board-certified plastic surgeon is crucial. The surgeon will also explain the types of implants, surgical techniques, and potential risks.
Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation, ensuring the patient is comfortable and pain-free.
Incision Options: Incisions can be made in inconspicuous areas to minimize visible scarring. Options include:
- Inframammary (under the breast)
- Periareolar (around the nipple)
- Transaxillary (in the armpit)
Insertion and Placement: After making the incision, the surgeon will insert the implant either under the pectoral muscle (submuscular placement) or directly behind the breast tissue (subglandular placement). The placement choice depends on the patient's body type, implant type, and desired outcome.
Closing the Incisions: The incisions are closed with layered sutures in the breast tissue, and with sutures, skin adhesive, or surgical tape to close the skin.
Recovery: Post-surgery, the breasts are wrapped in gauze dressings and an elastic bandage or support bra to minimize swelling and support the breasts as they heal. Patients are usually given detailed instructions on how to care for their breasts, medications to apply or take orally to aid healing, and follow-up appointments with the surgeon.
Recovery and Aftercare:
Recovery from breast augmentation surgery varies among individuals. Generally, patients can expect:
- Initial Recovery: The first few days post-surgery involve rest and limited movement. Swelling and discomfort are common but manageable with prescribed pain medications.
- Follow-Up: Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and address any concerns.
- Resuming Activities: Most patients return to work within a week, but strenuous activities should be avoided for at least 4-6 weeks.
- Long-Term Care: Regular self-examinations and routine check-ups with the surgeon ensure the implants' integrity and overall breast health.
Risks and Considerations:
As with any surgical procedure, breast augmentation carries potential risks, including:
- Implant leakage or rupture
- Capsular contracture (scar tissue that compresses the implant)
- Infection
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation
- Implant position changes
Choosing a board-certified plastic surgeon with extensive experience in breast augmentation can significantly mitigate these risks.
Conclusion:
Breast augmentation is a highly personal decision that requires careful consideration of the benefits, risks, and individual goals. With advancements in surgical techniques and implant technology, many women achieve their desired outcomes, enhancing their appearance and boosting their confidence. A thorough consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon is the first step toward making an informed decision about breast augmentation.
For more information visit Dynamic Clinic PK.