Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has revolutionized manufacturing processes across industries by automating and enhancing precision in production. CNC machining involves using pre-programmed computer software to control machining tools and equipment. Whether you're a beginner or looking to refine your skills, this guide will take you through the essentials of CNC machining.
Understanding CNC Machining
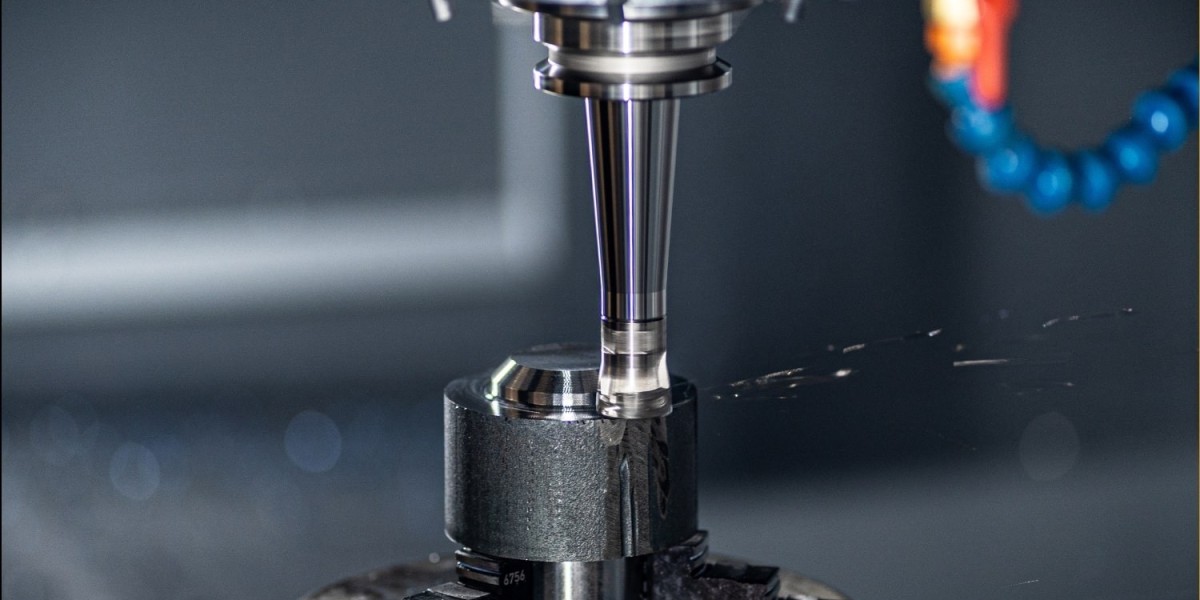
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process where raw material is cut away to create the desired shape. It's widely used for producing intricate parts with high accuracy. Here's how it works:
Design Phase: It starts with creating a 3D model of the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
CAM Programming: The CAD model is imported into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software where toolpaths are generated based on machining operations.
Machine Setup: The machinist sets up the CNC machine, installs the required tools, and loads the raw material.
Machining: The program is executed, and the CNC machine precisely cuts the material according to the specified toolpaths.
Finishing: After machining, the part may undergo finishing processes like deburring or surface treatment.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC Mills: These machines use rotary cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. They can perform tasks like drilling, cutting, and milling.
CNC Lathes: Lathes rotate the workpiece while cutting tools are applied to shape it. They are used for cylindrical parts and turning operations.
CNC Routers: Routers are similar to mills but are typically used for cutting softer materials like wood, plastic, or foam.
CNC Plasma Cutters: Ideal for cutting through electrically conductive materials using a plasma torch.
Key Techniques and Tips
Understanding Tooling: Choose the right cutting tools based on material and operation. Carbide tools are common for their durability.
Optimizing Feeds and Speeds: Adjusting cutting speed and feed rate optimally improves efficiency and surface finish while extending tool life.
Workholding: Securely hold the workpiece to prevent movement during machining. Various methods include clamps, vises, and fixtures.
Toolpath Optimization: Efficient toolpaths reduce machining time and tool wear. Avoid sharp direction changes and unnecessary movements.
Quality Control: Regularly measure parts using precision instruments to ensure they meet specifications.
Safety Precautions
Machine Safety: Follow all safety protocols while operating CNC machines. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Tool Safety: Handle cutting tools with care and ensure they are properly secured.
Material Handling: Use caution when handling sharp or heavy materials. Secure workpieces firmly.
Learning Resources
Online Tutorials: Websites like YouTube offer numerous tutorials covering CNC machining basics to advanced techniques.
Community Forums: Engage with CNC machining communities to learn from others' experiences and ask questions.
Books and Courses: Explore books and online courses tailored to CNC machining.
Manufacturer's Documentation: Refer to manuals and documentation provided by machine and tool manufacturers for specific guidance.
Conclusion
CNC machining is a versatile and precise manufacturing method with applications across various industries. Mastering CNC machining requires understanding the fundamentals, practicing techniques, and prioritizing safety. With dedication and practice, you can unlock the full potential of CNC machining for your projects.