Diesel engines have long been favored for their durability, fuel efficiency, and high torque, making them indispensable in transportation, construction, and agriculture. However, diesel engines are also significant contributors to air pollution, emitting particulate matter (PM) that poses serious health and environmental risks. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) have emerged as a crucial technology in controlling these emissions, playing a pivotal role in reducing the harmful impact of diesel engines on air quality.
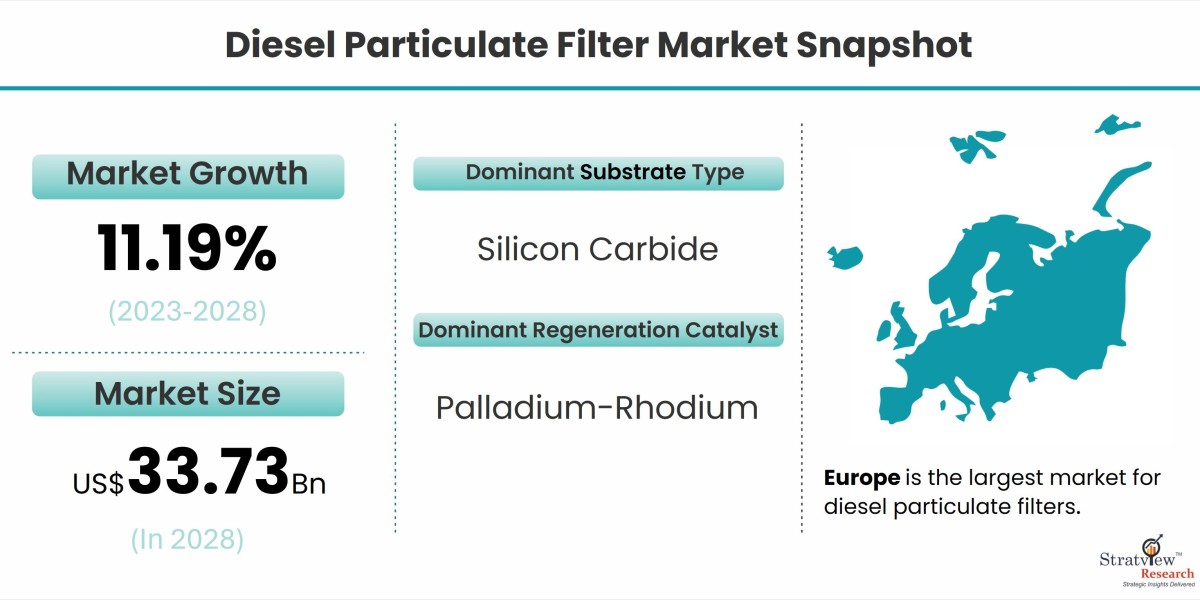
According to Stratview Research, the diesel particulate filter market was estimated at USD 17.8 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a healthy CAGR of 11.19% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 33.73 billion in 2028.
Understanding Diesel Particulate Filters
A Diesel Particulate Filter is a device designed to capture and store soot particles from the exhaust gas of a diesel engine. The primary function of a DPF is to reduce the amount of particulate matter released into the atmosphere. This is achieved through a filtration process where the exhaust gases pass through a porous ceramic material within the filter, trapping the soot particles while allowing the cleaned exhaust gases to pass through.
Mechanism of Action
The trapped soot in the DPF needs to be periodically removed to maintain the filter’s efficiency and prevent clogging. This process, known as regeneration, involves burning off the accumulated soot at high temperatures. Regeneration can occur passively, with the heat from the exhaust gases being sufficient to oxidize the soot, or actively, where additional fuel is injected to raise the temperature and ensure complete combustion of the particulates.
Benefits of Diesel Particulate Filters
1. Reduction of Particulate Emissions
DPFs are highly effective in reducing particulate emissions, capturing up to 85-95% of the soot particles produced by diesel engines. This substantial reduction significantly lowers the concentration of harmful PM in the air, contributing to improved air quality and public health.
2. Compliance with Emission Standards
Stringent emission regulations worldwide, such as the Euro 6 standards in Europe and Tier 4 standards in the United States, mandate lower levels of particulate emissions from diesel engines. DPFs are essential for meeting these regulatory requirements, ensuring that diesel vehicles and machinery operate within the legal emission limits.
3. Environmental Protection
By reducing particulate emissions, DPFs help mitigate the environmental impact of diesel engines. Lower emissions contribute to decreased smog formation, reduced acid rain, and overall better environmental health. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainable practices.
Challenges and Maintenance
While DPFs are effective in emission control, they require regular maintenance to function optimally. The regeneration process must be properly managed to prevent filter clogging and ensure long-term durability. Additionally, the initial cost of DPF installation and potential operational challenges, such as increased backpressure, can be barriers for some users.
Conclusion
Diesel Particulate Filters play a vital role in controlling emissions from diesel engines, significantly reducing the release of harmful particulate matter into the atmosphere. Their effectiveness in meeting stringent emission standards and improving air quality underscores their importance in modern emission control strategies. As technological advancements continue to enhance DPF performance and efficiency, their role in promoting cleaner air and a healthier environment will only become more critical.