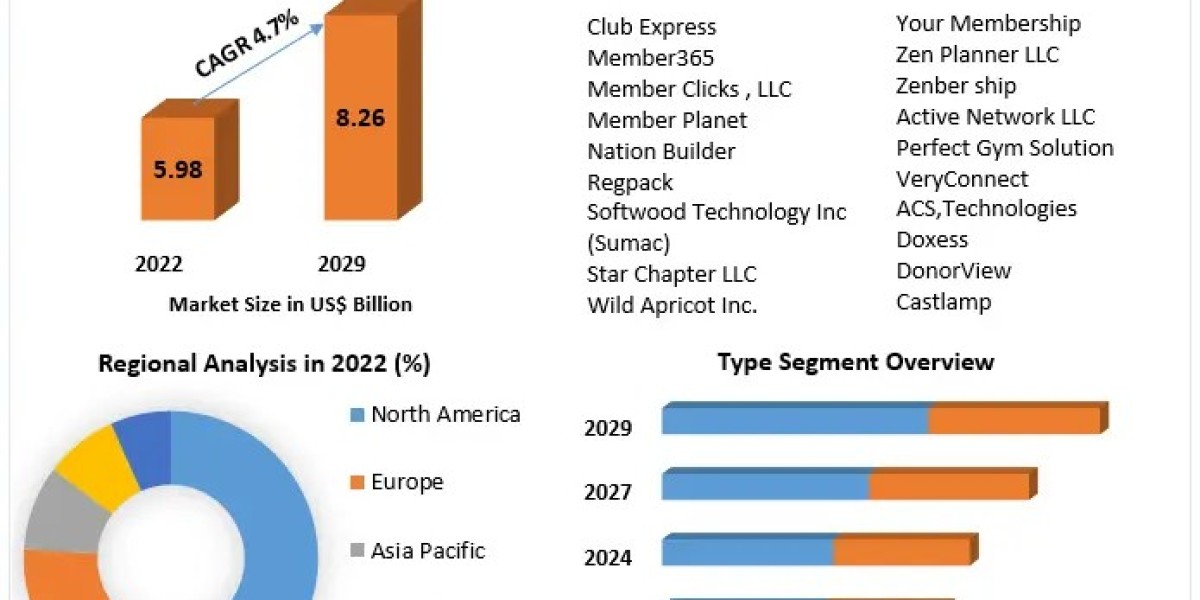
Motion graphics are a dynamic and captivating medium that blends design, animation, and storytelling. Behind the mesmerizing animations and transitions lies a set of principles that form the backbone of effective motion graphics. These principles of animation guide the creation of smooth, engaging, and visually appealing motion graphics that capture and hold the viewer's attention. Let's delve into the key principles that breathe life into motion graphics.
1. Timing and Spacing
One of the fundamental principles in animation is timing and spacing. It involves determining the speed at which an object moves and how it accelerates or decelerates. This principle is crucial in creating a natural and believable movement. Objects should move in a way that reflects real-world physics or artistic intent, ensuring that they don't appear rigid or robotic.
2. Anticipation
Anticipation is about preparing the viewer for an upcoming action. It involves a subtle movement or gesture that hints at what's about to happen. Anticipation adds context to the action and makes it more engaging and understandable. For instance, a character may lean back slightly before leaping forward, signaling their intent to jump.
3. Squash and Stretch
Squash and stretch are used to exaggerate the movement of objects, giving them a sense of weight, flexibility, and impact. When an object is in motion, it may stretch in the direction of its movement and squash upon impact or when it changes direction. This principle adds a dynamic and elastic quality to motion graphics.
4. Staging
Staging involves presenting the subject of an animation in a clear and visually appealing way. The composition, arrangement, and timing of elements on the screen should guide the viewer's attention and convey the intended message effectively. Proper staging prevents clutter and confusion, allowing the viewer to focus on the key elements.
5. Follow-Through and Overlapping Action
Objects rarely come to an abrupt stop in the real world. Follow-through and overlapping action refer to the way different parts of an object continue moving even after the main action is complete. This adds realism to animations and contributes to a more fluid and organic look.
6. Arcs
Most natural movements occur along curved paths, rather than straight lines. The principle of arcs emphasizes animating objects along smooth, curved trajectories. Applying this principle makes animations feel more natural and visually pleasing.
7. Secondary Action
Secondary actions complement the main action and add depth to animations. They might be smaller movements that occur simultaneously, providing context or enhancing the primary movement. These actions contribute to a richer and more engaging animation.
8. Exaggeration
Exaggeration is about pushing certain aspects of an animation to make it more entertaining or impactful. It's a technique commonly used in character animations to convey emotions or emphasize key actions. However, moderation is key to prevent animations from becoming too over-the-top.
9. Appeal
Appeal refers to the visual interest and attractiveness of characters, objects, and designs. In motion graphics, appealing characters or elements are more likely to capture the viewer's attention and keep them engaged. This principle ties closely to design aesthetics.
10. Consistency
Consistency ensures that the visual style, movement, and behavior of objects remain uniform throughout an animation. This principle is vital for creating a coherent and harmonious motion graphics piece.
Conclusion
Mastering the principles of animation in motion graphics empowers designers to create animations that resonate with audiences on a profound level. By understanding and applying concepts like timing and spacing, anticipation, and squash and stretch, motion graphic expert can breathe life into their creations. Whether it's a short promotional video, an explainer animation, or a complex visual narrative, these principles are the building blocks that transform static designs into dynamic, captivating stories.